Whiplash Symptoms – More Than Just Neck Pain
Whiplash is usually caused by motor vehicle accidents, most commonly what is called a rear end collision, where the neck is suddenly and forcibly extended back by the force of the accident. A secondary forward flexion force results in a rebound effect as the neck whips forward. These movements will typically be beyond the normal range of movement of the neck, and thus whiplash symptoms may relate to damage to bones, joints, soft tissues and nerves.
Some sporting injuries or forceful incidents involving the neck may also have the same effect, and create similar symptoms.
Following a whiplash injury, there are a number of symptoms which may result. These symptoms are often called “Whiplash Associated Disorders” or WAD.
After suffering a whiplash injury, it is possible that symptoms might not be noticed for 48 to 72 hours after the accident. These symptoms might be:
- neck pain
- pain in the upper back and/or shoulder blades
- numbness/tingling
- headaches
- head feeling heavy
- pain and/or weakness in the arm
- nausea
- back pain
 As time progresses, depression and other psychological issues may arise, and are often blamed for ongoing symptoms.
As time progresses, depression and other psychological issues may arise, and are often blamed for ongoing symptoms.
Neck Pain can be very difficult to treat effectively, with a significant proportion of the population going on to suffer Chronic Neck Pain or pain lasting longer than 6 months duration.
After a whiplash injury, examinations such as x-ray, CT (computerized tomography) or MRI may be performed, which will usually come up “normal”. This does not necessarily mean that there is no problem, these examinations are sometimes unable to detect certain problems.
Physical examinations usually include neck mobility, strength, and nerve function, and treatment is usually directed for any deficits found.
Whiplash Symptoms Questionnaire
This questionnaire has been designed to provide information on how much pain you experience on a day-to-day basis following your trauma. Noticing a change of 19 points would be important, so this can help to determine if your symptoms are improving, staying the same or getting worse. It can give you an initial score for symptom severity, but the important thing is change, hopefully for the better. So check back as often as you like, once a month for ongoing analysis and documentation.
Please answer every section below and for each category, please indicate the severity of the symptom using the 1-10 point scale where:
1 = No Symptoms
10 = Extreme Symptoms
After answering ALL of the items click on the ‘Score‘ button for your score.

Neck Weakness
Many people suffering from whiplash symptoms will often describe the feeling of a “Heavy Head”. The head feels as though it is too heavy for the neck to hold up and there will b difficulty in being able to lift their head off the pillow, or of having to use their hands to support their head at times. This “Heavy Head” is usually and indication of weakness of the muscles which support the neck and head. This weakness may arise from nerve damage, muscle damage, poor posture or repetitive activities. The muscles may be inhibited by pain or nerve problems, or fatigue may set in towards the end of an activity. Muscles of the neck become weakened following trauma, such as Whiplash and Sporting Accidents or prolonged poor neck posture, especially working over a computer or desk. Ongoing neck pain and discomfort often leads to altered or disturbed movement patterns, reduced physical activity and ultimately further neck weakness.
Headaches
A headache generally is among the most incapacitating symptoms involved with whiplash injuries as well as other neck troubles. “Cervicogenic Headache” indicates headaches triggered by problems with the joints, muscle tissues or nerves which are neck associated headaches. There are various presentations with pain locations which may be at the front in the head (frontal headaches), to one or both sides (temporal headaches), or even the base of the back of the head (occipital headaches).
Symptoms like throbbing, aching, blinding or even crushing are sometimes noted and symptoms might last several hours, days or perhaps months at one time. Trauma like a whiplash injury or even sports injuries to the neck may cause these types of headaches. Repeated motions or harmful postures (e.g. seated at a laptop or desktop computer throughout the day) also can irritate the neck with time and these particular causative factors have to be solved to assure continuing pain relief. You should determine just what makes symptoms worse. Such things as computers, driving a vehicle or heavy-lifting may suggest a neck associated aspect to the headaches, whereas eating particular foods or not getting sufficient water may feature a different kind of headache, not related to whiplash.
A 2023 study in Musculoskelet Science & Practice indicates headaches related to whiplash appear to be mild to moderate in intensity, typically short duration episodes, often experienced in the occipital (back of head) region as well as other regions, and have a tendency to reduce in severity over time.
Arm Pain or Weakness
Many people suffering from whiplash symptoms may have arm pain or weakness, usually only on the side relating to the dysfunction in the neck. In most cases, the arm pain or weakness is only present when the neck has been aggravated in some way, and will not be there at all time. The type and location of symptoms will vary with different people, however there are 4 basic areas – the shoulder, above the elbow, above the wrist and below the wrist. There may be symptoms in only one or all four areas.
The most common cause of neck related arm pain or weakness is an irritation of the nerves which supply the arm. These nerves arise from the neck region, and can easily become irritated by dysfunction in the neck. Arm Pain may originate from sensory nerves supplying the skin of the arm and is felt in very specific areas called “dermatomes” relating to the supply pattern of specific nerves which often affect the fingers and hand. Muscular Weakness in the arm may be related to irritation of the nerves supplying the muscles of the arm that have specific nerve supplies which may be determined by looking at which muscles are weakened. A thorough assessment by your Health Practitioner should determine the spinal level of the trauma.
Pins & Needles or Numbness
Many sufferers of whiplash will report feeling pins and needles or numbness in the hand or arm of the affected side. It may be intermittent – comes and goes, or may be present for days or weeks on end. The cause of altered sensation in the arm is irritation of the nerves. This irritation may occur at any level and most often involve the roots of the nerves which exit between the spinal bones. The nerve roots are the point where the nerves which supply the different areas of the neck and arm arise from the spinal cord.
The neck has 8 nerve roots which exit from the spinal column through small gaps between the vertebrae and if these gaps are reduced in size, perhaps by a problem with the joint, muscle or disc, the nerve roots may be irritated. This will cause changes in sensation along the entire path of the nerve, usually more so at the very end of the nerve at the fingers and hand.
Back Pain
A 2020 review in Accident Analysis & Prevention found positive associations for the risk of future lower back pain after an motor vehicle related injury. For those with chronic low back pain and initially injured in an accident, about 63% of the time the condition was caused by the accident.
Psychological Problems
Chronic whiplash is a significant problem for those who have poor recovery and ongoing symptoms. Distressful psychological problems are often seen, like depression, anxiety and and posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Initially the distress experienced by individuals suffering whiplash improves as pain and disability improves, while it remains high in those who do not have relief of pain and improvement in their daily life and/or work activities.
Pain catastrophizing is another psychological issue in those with chronic pain with exaggeration of pain response and is associated with high pain reports, poor prognosis for recovery and disability. Cognitive behavioral therapy is often used to address these psychological symptoms and has been shown to have some improvement on helping individuals deal with these ongoing symptoms, however, this does not remove the pain.
In a 2014 edition of Pain Physician journal, the authors used a technique called cervical radiofrequency neurotomy, which essentially eliminates the sensory nerves of the joints in the neck that are often responsible for ongoing pain and dysfunction. These joints are are the facet joints, and often cause pain similar to a disc problem or pinched nerve in what is termed facet syndrome. Treatment with this method has been shown to help with pain, neck mobility and disability. In those with chronic whiplash, it has been demonstrated to also help with distress as well as anxiety.
The results of the study indicated that the procedure had a significant effect, helping with pain catastrophization, psychological distress, disability and pain, but did not help but not posttraumatic stress symptoms. Nonetheless, the study showed that effective pain relief is an important element for managing psychological problems associated with chronic whiplash symptoms.
You should always have an examination by a health care provider for any symptoms. For relief of pain, a number of treatments may be used. These include medications for neck pain (anti-inflammatories or analgesics), electrotherapy (TENS Units), temporary rest from aggravating activity, massage, ice or heat. Weakness of the neck muscles can be addressed with neck exercises. Other methods of treatment are manipulation or specific adjustments of the joints, traction, stretching of the nerves and muscles, acupuncture and other forms of non-surgical neck pain treatment.
There are many ways to help yourself to obtain the best results for whiplash recovery. For those with chronic symptoms and difficulty dealing with them, please see managing whiplash.
Products To Help Whiplash Symptoms
A 2021 study in the Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy found that hyper-arousal symptoms may predict poor recovery after whiplash injury. These symptoms include feeling irritable or prone to getting angry easily, difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep, difficulty concentrating, being noticeably overly alert, and feeling jumpy or easily startled.
A 2021 study in PLoS One found changes in joint position sense and standing balance confirms deficits in the sensory and motor control in people with whiplash and especially in those with dizziness.

 Neck Traction Devices
Neck Traction Devices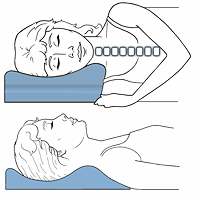 Cervical Pillows
Cervical Pillows Neck Support Collars
Neck Support Collars Muscle Therapy Tools
Muscle Therapy Tools Head Supports
Head Supports Topical Pain Relievers
Topical Pain Relievers Special Pillows
Special Pillows Heat Therapy
Heat Therapy Cold Therapy
Cold Therapy TENS Therapy
TENS Therapy Posture Braces
Posture Braces Neck Stabilization
Neck Stabilization Ergonomic Aids
Ergonomic Aids New Mattresses
New Mattresses Relief Supplements
Relief Supplements